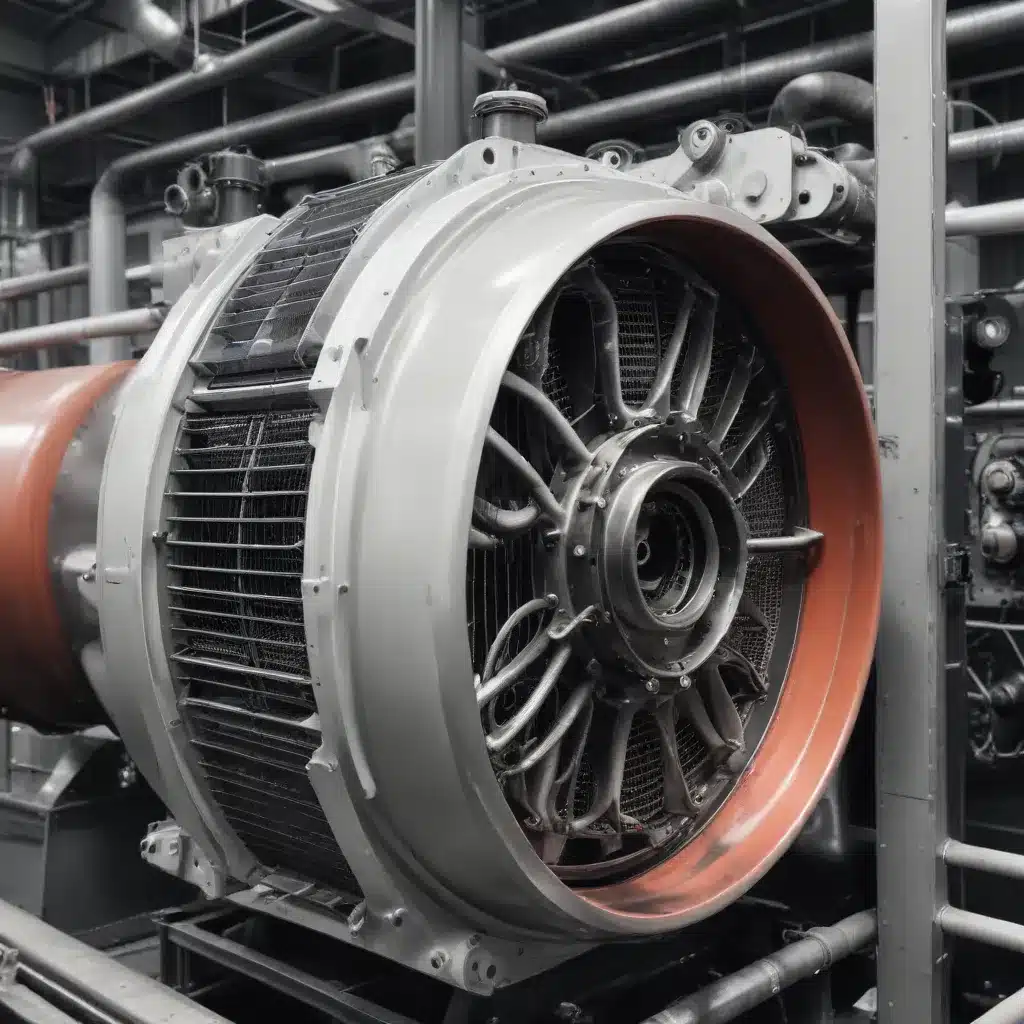
Understanding the Importance of Proper Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger Maintenance
Air-cooled heat exchangers are a critical component in a wide range of industrial applications, from power generation and petrochemical processing to HVAC systems and manufacturing equipment. These robust units play a pivotal role in transferring heat efficiently, ensuring optimal performance and productivity across diverse industries. However, ensuring the safety, compliance, and reliable long-term operation of air-cooled heat exchangers requires a comprehensive maintenance and inspection program tailored to the unique demands of each application.
As an experienced expert in this field, I understand the importance of proactive maintenance strategies, regulatory adherence, and a deep understanding of air-cooled heat exchanger design, materials, and failure modes. In this article, I will provide practical guidance and in-depth insights to help machinery and equipment manufacturers safeguard their operations, minimize downtime, and extend the lifecycle of their air-cooled heat exchanger systems.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Air-cooled heat exchanger maintenance and operation must adhere to a range of safety regulations and industry standards to ensure the protection of personnel, assets, and the environment. Key compliance considerations include:
Occupational Health and Safety
The IFC General EHS Guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for managing workplace health and safety risks, including those associated with the use of air-cooled heat exchangers. Relevant guidelines cover topics such as:
- Hazard identification and risk assessment
- Preventive and protective measures (e.g., engineering controls, personal protective equipment)
- Emergency preparedness and response
- Occupational health monitoring and surveillance
Adherence to these guidelines helps safeguard workers from potential hazards like hot surfaces, fan blade injuries, and exposure to leaks or emissions.
Environmental Compliance
Regulations such as the SECNAV Instruction 5100.19F outline requirements for the proper handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials associated with air-cooled heat exchanger maintenance, including lubricants, cleaning solvents, and coolants. Ensuring compliance in these areas helps prevent environmental contamination and safeguard the health of both workers and the surrounding community.
Materials and Equipment Integrity
Adherence to industry standards, such as those published by organizations like the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the American Petroleum Institute (API), is critical for maintaining the structural integrity and performance of air-cooled heat exchanger components. These standards provide guidance on design, fabrication, inspection, and testing protocols to ensure the equipment’s safe and reliable operation throughout its lifecycle.
By prioritizing regulatory compliance and industry best practices, machinery and equipment manufacturers can mitigate risks, protect their workforce, and demonstrate a strong commitment to environmental stewardship.
Comprehensive Maintenance and Inspection Strategies
Developing and implementing a comprehensive maintenance and inspection program is essential for ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of air-cooled heat exchanger systems. This program should encompass the following key elements:
Preventive Maintenance
Routine preventive maintenance tasks, such as regular cleaning, lubricating, and inspecting critical components, help identify and address potential problems before they lead to equipment failure or unplanned downtime. Establishing a detailed preventive maintenance schedule, based on manufacturer recommendations and operational conditions, is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and extending the service life of air-cooled heat exchangers.
Condition Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Incorporating advanced condition monitoring techniques, such as vibration analysis, thermography, and oil analysis, can provide early warning signs of impending issues, enabling proactive maintenance and repairs. By leveraging predictive maintenance strategies, manufacturers can optimize their maintenance schedules, minimize unexpected breakdowns, and maximize the return on their air-cooled heat exchanger investments.
Lifecycle Management and Asset Tracking
Effective air-cooled heat exchanger lifecycle management involves maintaining detailed records of each unit’s installation, service history, and performance data. This information can be used to identify recurring problems, track component replacement schedules, and make informed decisions about equipment upgrades or replacements. Integrating asset management systems and utilizing CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) software can streamline these processes and provide valuable insights for optimizing maintenance practices.
Training and Competency Development
Ensuring that maintenance personnel are properly trained and competent in the safe handling, inspection, and repair of air-cooled heat exchangers is essential for maintaining compliance and minimizing safety risks. Comprehensive training programs, regular skill assessments, and the implementation of standardized work procedures can help develop a highly skilled workforce capable of effectively maintaining these critical systems.
By implementing a holistic maintenance and inspection program, machinery and equipment manufacturers can maximize the reliability, efficiency, and longevity of their air-cooled heat exchanger assets, contributing to increased productivity, reduced operational costs, and enhanced compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
Optimizing Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger Performance and Reliability
In addition to comprehensive maintenance and inspection strategies, there are several design-related considerations that can help optimize the performance and reliability of air-cooled heat exchanger systems:
Material Selection and Corrosion Resistance
Choosing the appropriate materials for air-cooled heat exchanger components, such as the tubes, fins, and headers, is crucial for ensuring long-term durability and resistance to corrosion. Factors like the operating environment, fluid composition, and thermal stresses must be carefully evaluated to select the optimal materials, which may include stainless steel, aluminum, or specialized alloys.
Fin Design and Airflow Optimization
The design of the heat exchanger fins, including their material, thickness, and spacing, can significantly impact the unit’s thermal efficiency and air-side pressure drop. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling can help identify the optimal fin configuration to maximize heat transfer while minimizing the energy required for airflow.
Fouling and Cleaning Considerations
Air-cooled heat exchangers are susceptible to fouling, which can reduce heat transfer efficiency and increase pressure drop. Designing the heat exchanger with easy access for cleaning, as well as incorporating features like smooth fin surfaces and periodic self-cleaning mechanisms, can help mitigate the impact of fouling and simplify maintenance procedures.
Vibration and Structural Integrity
Air-cooled heat exchangers must be designed to withstand the dynamic loads and vibrations experienced during operation. Proper structural analysis, the use of anti-vibration mountings, and the incorporation of damping mechanisms can help prevent premature failure and ensure the long-term reliability of these systems.
By addressing these design-related factors, machinery and equipment manufacturers can enhance the overall performance, efficiency, and service life of their air-cooled heat exchanger assets, ultimately contributing to improved productivity, reduced maintenance costs, and increased compliance with industry standards.
Leveraging Expertise and Resources for Effective Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger Maintenance
Maintaining the optimal performance and compliance of air-cooled heat exchanger systems often requires the expertise of specialized service providers and access to comprehensive resources. Some key considerations in this area include:
Engaging Qualified Service Providers
Partnering with experienced air-cooled heat exchanger service providers can be invaluable for ensuring proper maintenance, repairs, and troubleshooting. These specialized firms can offer a range of services, such as inspections, condition assessments, maintenance planning, and the procurement of genuine replacement parts.
Accessing Comprehensive Technical Resources
Leveraging comprehensive technical resources, such as manufacturer-provided maintenance manuals, industry guidelines, and online forums, can help maintenance personnel stay up-to-date with the latest best practices, safety protocols, and troubleshooting techniques for air-cooled heat exchangers.
Continuous Education and Training
Investing in ongoing education and training for maintenance teams is crucial for adapting to evolving industry standards, technological advancements, and emerging maintenance strategies. Participation in industry conferences, webinars, and specialized training programs can help ensure that personnel remain competent and equipped to handle the complex challenges associated with air-cooled heat exchanger maintenance.
By proactively engaging with qualified service providers, accessing comprehensive technical resources, and prioritizing continuous education and training, machinery and equipment manufacturers can optimize the performance, reliability, and compliance of their air-cooled heat exchanger systems, ultimately contributing to the long-term success and sustainability of their operations.
Conclusion
Ensuring the proper maintenance, inspection, and lifecycle management of air-cooled heat exchanger systems is a critical imperative for machinery and equipment manufacturers across diverse industries. By prioritizing regulatory compliance, implementing comprehensive maintenance strategies, optimizing design considerations, and leveraging specialized expertise and resources, these organizations can safeguard the safety of their workforce, minimize operational disruptions, and maximize the return on their air-cooled heat exchanger investments.
As an experienced expert in this field, I encourage all machinery and equipment manufacturers to review their existing air-cooled heat exchanger maintenance practices, identify areas for improvement, and take proactive steps to enhance the reliability, efficiency, and compliance of these mission-critical systems. By doing so, they can position themselves for long-term success, competitive advantage, and a sustained commitment to operational excellence.
For more information and practical insights on air-cooled heat exchanger maintenance and lifecycle management, I invite you to explore the resources available on our Air Cooled Heat Exchangers website.

